Risks of antibiotic manufacturing pollution for the spread of Antimicrobial Resistance

What is AMR?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing public health concern that occurs when microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, become resistant to the drugs designed to kill them. This can lead to serious infections that are difficult to treat, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. One of the potential sources of AMR is pollution from manufacturing facilities that produce antimicrobials.
Antibiotics manufacturing led AMR
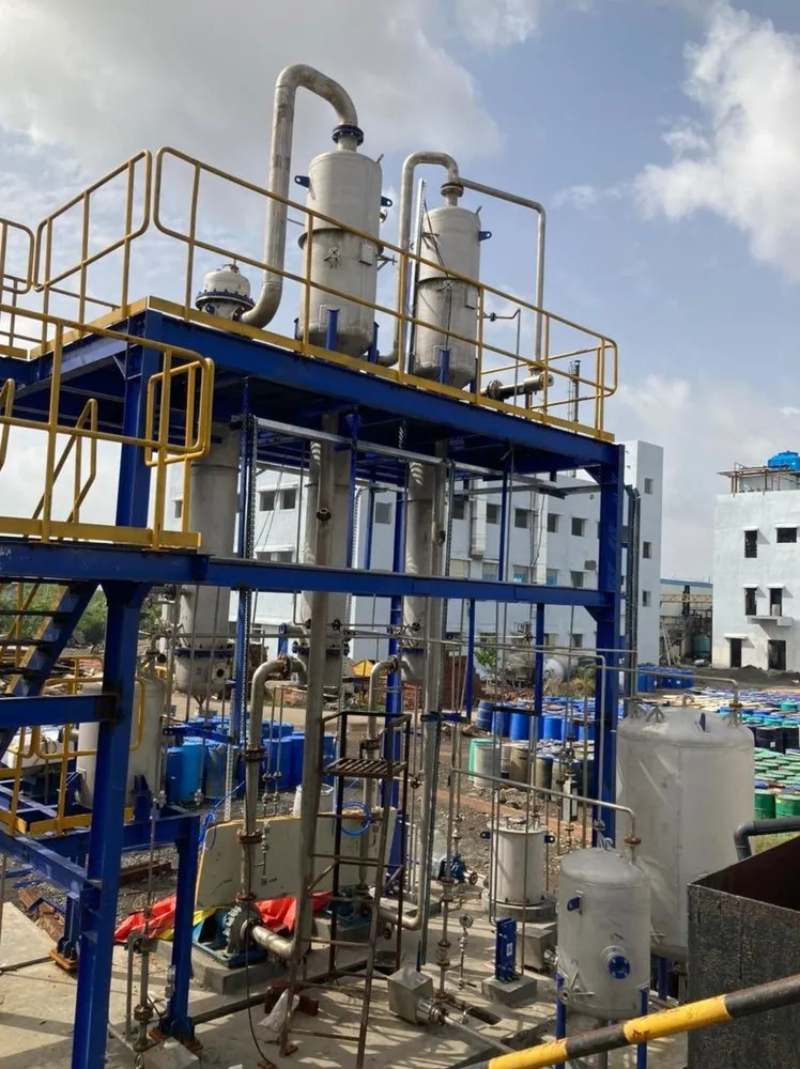
Manufacturing facilities that produce antimicrobials can release these substances into the environment through their waste streams, including air emissions and wastewater discharges. These releases can occur during the production process, as well as during the transportation, storage, and disposal of antimicrobials.
The release of antimicrobials into the environment can lead to the development of resistant bacteria in natural ecosystems, such as soil, water, and air. These bacteria can then spread to humans and animals through various routes, including the food chain and direct contact. The presence of antimicrobials in the environment can also disrupt the balance of microbial communities, leading to the emergence of new resistant strains.
One of the main risks of AMR from manufacturing pollution is the potential for the development of multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria. MDR bacteria are resistant to several different classes of antimicrobials, making them difficult to treat and potentially leading to serious infections. The spread of MDR bacteria can also lead to the emergence of new resistant strains, further increasing the risk of AMR.
Another risk of AMR from manufacturing pollution is the potential for the transmission of resistant bacteria from animals to humans. Many antimicrobials are used in animal agriculture, and the release of these substances into the environment can lead to the development of resistant bacteria in animals. These bacteria can then be transmitted to humans through the food chain, or through direct contact with animals.
In addition to the risks posed by AMR from manufacturing pollution, there are also economic costs associated with the use and release of antimicrobials. The overuse and misuse of antimicrobials can lead to the development of resistant bacteria, which can increase healthcare costs and reduce the effectiveness of these drugs.
To address the risks of AMR from manufacturing pollution, it is important for manufacturers to implement proper waste management practices to minimize the release of antimicrobials into the environment. This can include the use of closed-loop systems and advanced treatment technologies to reduce the amount of antimicrobials released into the environment. It is also important for governments to regulate the use and release of antimicrobials, and for individuals to follow proper hygiene practices to reduce the spread of resistant bacteria.
Overall, the risks of AMR from manufacturing pollution are a serious concern that must be addressed to protect public health and reduce the economic costs associated with the spread of resistant bacteria. By taking steps to minimize the release of antimicrobials into the environment and properly managing their use, we can help reduce the risk of AMR and protect against the spread of resistant bacteria.
Collaboration Opportunities in India
Spansis working with innovators and global impact investors to better understand the challenges, risks, and mitigation strategies. Some of the key projects we are working on include:
- Responsible Antibiotics Manufacturing Platform (RAMP) - Spans is the Indian partner to the responsible antibiotics manufacturing platform. RAMP is leading the industry transformation towards responsible antibiotic manufacturing to reduce the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
- EU-India Water Partnership - The European Union is conducting independent market research on the status of antibiotic manufacturing and the role of responsible antibiotic manufacturing as a way to reduce the spread of AMR in India. Based on the market study further investment decisions are expected to be taken to leverage the India-EU water partnership for joint efforts toward combating Antimicrobial Resistance.
- Spans is supporting the Netherlands Innovation Mission to develop a landscape of opportunities for India-Dutch collaboration specifically focusing on technologies and know-how of Dutch companies to help Indians combat AMR. The project is evaluating various opportunities across three sectors including antibiotics manufacturing, hospital wastewater management, and the presence of antibiotics in domestic sewage.
If you would like to learn more about our projects and/or would like to collaborate with us, please write to us at [email protected].