Environmental Best Practices in Rice Processing: Focus on Water and Wastewater Management
Rice is one of the most widely consumed staple foods globally, with its production processes often involving substantial water use. The water footprint of rice processing, from cleaning and soaking to milling and polishing, can result in significant wastewater generation. Managing this water efficiently and reducing the environmental impact of wastewater discharge is essential for sustainable rice processing.
In this blog, we will explore the best environmental practices in rice processing, focusing on innovative methods for water conservation and wastewater treatment to promote sustainability in the industry.

Water Usage in Rice Processing
Rice processing is water-intensive, with water being used at nearly every stage of production. The two primary stages where water plays a critical role are the soaking and milling processes:
Soaking: The initial step in rice processing involves soaking the raw grains to soften them and facilitate the husking and milling stages. Soaking requires a significant amount of water, which can often lead to wastewater loaded with organic matter like starch and husks.
Milling and Polishing: The subsequent milling and polishing processes use water to cool machinery, clean the rice, and remove bran layers from the grains. This water, once used, often becomes contaminated with rice bran, husk particles, and other organic residues.
Given the large quantities of water used, implementing water conservation strategies and proper wastewater treatment is crucial to reducing the environmental footprint of rice processing facilities.
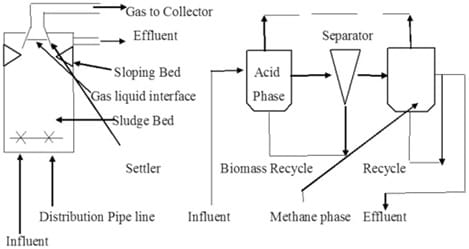
Wastewater Treatment Practices in Rice Processing
The wastewater generated in rice processing contains organic materials, starch, oils, and other byproducts. If not properly treated, this wastewater can contribute to environmental pollution, particularly in nearby water bodies. Here are some best practices for wastewater management in rice processing facilities:
Starch and Husk Recovery
Rice processing wastewater often contains high concentrations of starch and rice husk residues. Instead of discharging these valuable byproducts, rice processors can implement starch recovery systems that filter out starch from the wastewater. This recovered starch can be reused in other food products or sold to industries that utilize it, reducing waste and creating an additional revenue stream. Similarly, rice husks can be repurposed as biofuel or used in agricultural applications as a sustainable alternative to disposal.
Biological Treatment Systems
One of the most effective methods for treating organic wastewater in rice processing is the use of biological treatment systems, such as anaerobic digestion or activated sludge processes. These systems rely on microorganisms to break down organic matter, reducing the pollutant load in wastewater before it is discharged or reused.
- Anaerobic digestion is particularly useful in rice processing as it not only treats wastewater but also generates biogas, which can be used as a renewable energy source within the facility. This dual benefit reduces both the environmental impact of wastewater and the facility's reliance on non-renewable energy.
Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration is an advanced method for treating wastewater in rice processing plants. This process involves passing wastewater through semi-permeable membranes that filter out contaminants, including solids, oils, and organic materials. The treated water can be recycled and reused for non-potable purposes, such as equipment cooling or initial cleaning stages, drastically reducing the need for fresh water in the facility.
Water Conservation Strategies
In addition to wastewater treatment, rice processing facilities can adopt water conservation practices to minimize overall water use. By incorporating efficient water management systems, facilities can significantly reduce their water footprint.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rice processing plants in areas with significant rainfall can install rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses such as machinery cleaning, cooling systems, and dust suppression. This practice not only conserves freshwater resources but also reduces the facility's reliance on municipal water supplies, thereby lowering operational costs.
Energy Efficiency and Water Use
Rice processing facilities can also improve their overall sustainability by combining water conservation with energy efficiency measures. By reducing the energy required for water heating, pumping, and treatment, facilities can further lower their environmental impact.
Heat Recovery from Wastewater
Heat recovery systems can be installed to capture and reuse the heat from hot wastewater generated during the rice milling process. This heat can be used to preheat water for other stages of production, reducing the energy demand for heating and saving both water and energy in the process.
Reducing Environmental Impact through Innovation
Many rice processing facilities are now leveraging smart technologies and data-driven insights to improve their water management practices.
Real-time water monitoring systems can detect leaks or inefficiencies in water use, allowing operators to make immediate adjustments and optimize water consumption throughout the production cycle.
Artificial intelligence and IoT-based solutions can further enhance water conservation efforts by predicting water usage patterns, optimizing wastewater treatment systems, and reducing water waste during production processes.

Educating Producers and Consumers on Sustainable Practices
Sustainability in rice processing is not only about adopting environmentally friendly practices at the facility level. It also involves educating rice producers and consumers about sustainable practices.
Farmers can be encouraged to adopt water-efficient irrigation methods such as drip irrigation or alternate wetting and drying (AWD), which reduces water usage during rice cultivation.
Consumers can also be made aware of the importance of choosing rice products from environmentally conscious producers, thereby supporting sustainable practices in the rice industry.
Conclusion
Sustainable rice processing requires a holistic approach that prioritizes water conservation and effective wastewater treatment. By implementing advanced wastewater treatment systems, optimizing water use in production, and leveraging innovative technologies, rice processing facilities can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. As water scarcity becomes an increasing global concern, these practices not only help protect vital water resources but also position the rice industry as a leader in sustainable food production.